
Weighted Mean Calculator is an online statistics tool for data analysis programmed to calculate the Weighted Mean by giving different weights to some of the individual values. These are the familiar formulas, showing that the calculation for weighted data is a direct generalization of them. The example shows that the mean or average return for the observed value is 41.47. Since the $X_i$ are independent and each one has variance $\text$. In a simple random sample $X_1, \ldots, X_n$ where each $X_i$ independently has a Bernoulli$(p)$ distribution and weight $\omega_i$, the weighted sample proportion is Standardize the (positive) weights $\omega_i$ so they sum to unity. Take the square root of the calculated value. The sample proportion is the number in the sample with the characteristic of interest, divided by n. Binomial proportion confidence interval on Wikipedia.Yes, this formula generalizes in a natural way. Here are the steps for calculating the margin of error for a sample proportion: Find the sample size, n, and the sample proportion. However, standard errors exist for other population parameters, such as the population proportion, correlation, regression coefficients, etc.To do by hand is easy because use of table(v1, v2), but I dont want to do by hand :) Said in more simple way: I want to find but we can use mean as it is numeric variable. About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy & Safety How YouTube works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us Creators.
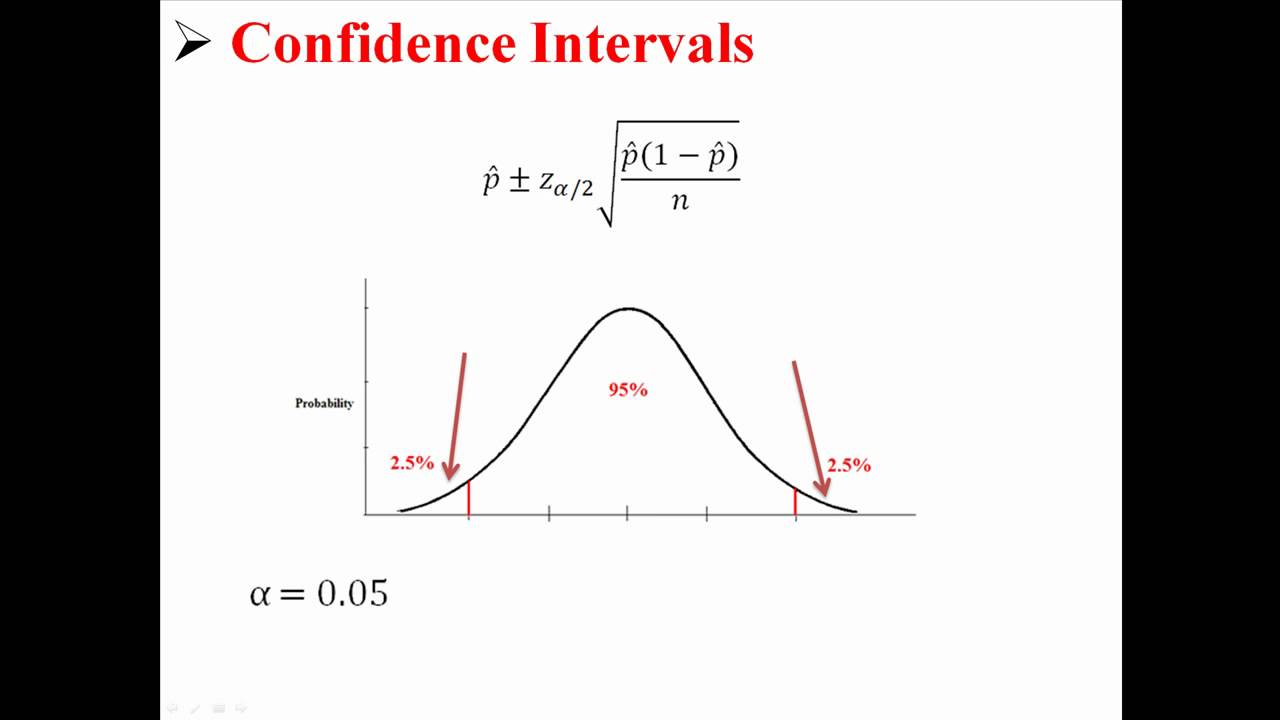

The P-value is the area of the normal distribution that falls outside ± z (see Values of the Normal distribution table). The standard error of a proportion is a statistic indicating how greatly a particular sample proportion is likely to differ from the proportion in the. Where p is the observed proportion p exp is the Null hypothesis (or expected) proportion and se( p) is the standard error of the expected proportion: The significance level, or P-value, is calculated using a general z-test (Altman, 1991): Null Hypothesis value (%): the pre-specified proportion (the value to compare the observed proportion to), expressed as a percentage.Sample size: the sample size or total number of observations.Observed proportion (%): the observed proportion, expressed as a percentage.This test is not performed on data in the data table, but on statistics you enter in a dialog box. The Test for one proportion can be used to test the hypothesis that an observed proportion is equal to a pre-specified proportion.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
